The Future of Power Generation: V2G Charging

Vehicle to Grid (V2G) charging is the best way to balance the unpredictable power output from renewable energy sources. In this model, renewable energy is stored in electric vehicles when the energy generation is higher than the demand. When there is not enough renewable energy produced, the power flows in the opposite direction: from vehicle to grid.
What is Vehicle To Grid Charging?
Vehicle to Grid Charging or the vehicle to grid technology enables electric cars to be used even when not driven. The bidirectional charging means that your EV battery is being charged from renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power, during peak production.
On the other hand, the energy demand spikes when people return back home. This time usually falls between 5 and 7 PM. During this time, the sun sets and renewable energy generation drops.
At the moment, electric vehicles take over at least part of the energy demand and use battery capacity to send power from vehicle to grid. This is the basis of bidirectional charging. Under this model, the sudden spikes in energy production and consumption are flattened and the grid is kept more stable.
Your EV battery charges when energy production is at its highest and it releases energy when energy consumption peaks. Power companies love this technology. They can rely less on power plants and fossil fuels to deliver power to you.
What is V2G?
V2G is the Vehicle To Grid technology. It enables solar energy and wind energy to be stored in your EV battery when you do not drive your vehicle. When there is a spike in energy demand, your vehicle sends power to the grid, so that renewables can make up a larger portion of the energy mix you use.
What is V2X?
V2X is a bidirectional charging technology that allows any object or device to be charged from your car batteries. EV battery capacity is quite high, so high actually that it can power an average home for around 3 days non-stop if the house uses <30 kWh of energy per day. This is around the US average.
The V2X technology is further branched into:
- V2H – Vehicle to House,
- V2B – Vehicle to Building, and
- V2G – Vehicle to Grid.
In the V2H model, your EV can store enough power to run your house for at least 2 days* and still have enough power for you to drive to work. The only prerequisite is that the car has smart charging enabled. In smart charging, your car’s internal electronics are bypassed. An external system controls the flow of solar power or other forms of power to and from plug-in electric vehicles.
* – assuming a 100 kWh battery
Importance of V2G
This new vehicle to grid technology, also known as the V2G bidirectional charging, offers multiple benefits over the traditional energy system:
- Electric vehicles are useful even when you do not drive them,
- The electrical grid is less vulnerable to momentary electricity consumption spikes,
- There is no need to start and shift reserve power plants.
Furthermore:
- Remote locations are protected in extreme weather events,
- The power grid is protected in case of a blackout – individual homes and buildings stay powered,
- The energy efficiency of the entire grid is improved,
- Renewable energy is better utilized and less energy is wasted.
What Are The Types of V2G?
There are three basic types of V2G or vehicle to grid. In all three models, the ability of your car to store energy is relied on to ease the burden on power plants and use your car’s batteries for grid balancing. This keeps energy prices low and increases the renewable energy production efficiency. The three types of V2G are:
- Unidirectional V2G or V1G – under this model, the energy flow is only from the grid to your electric vehicle. Your EV battery is charged only when there is a surplus of energy produced in renewable energy power plants. This type of smart EV charging means that vehicles can be used to balance the grid frequency and improve energy stability.
- Bidirectional local V2G – this type of vehicle to grid technology does not interfere with the entire grid, but it rather takes care of the local energy needs. During the day, your solar panels produce energy, and any energy that is not used is sent to EVs to store energy for later use. Your car battery life is not impacted and your home is kept powered up. In a model like this, you only rely on the grid to provide extra energy during spikes of use. There are two types of bidirectional local V2G: Vehicle to home (V2H) and vehicle to building (V2B).
- Bidirectional V2G – A more general approach to vehicle to grid, this model influences the grid and the power that runs through it. These work models enable your energy system administrator to both store energy in your EV battery and to draw from it, depending on the need.
What Are The Benefits of V2G?
There are many benefits of the vehicle to grid for both EV owners and grid operators, especially if done on a larger scale. The grid V2G technology offers benefits for consumers, power grids, and residential buildings.
For Consumers
Under the bidirectional local grid V2G technology, consumers can enjoy knowing all their solar power is put to good use. This system can reduce energy losses due to overproduction during sunny days. The excess energy is stored during EV charging and released when there is no more sunshine. This model helps mitigate climate change and keeps your power bill low.
Other benefits, especially in bidirectional grid V2G technology are that your EV can be used to balance the network and your power company may decide to offer a clear incentive for doing so. Getting paid to leave your EV charging, plugged in the DC charger throughout the day, was never this feasible.
For Power Grids
As renewable energy is volatile and hard-to-predict, EV charging can be used to balance the grid and avoid the Texas scenario. When more energy is produced than is consumed, your EVs can store energy and balance the energy system. In the opposite case, when the consumption is higher than the production, the smart charging technology reverses the direction of energy flow and supplies the needed energy to the power grid. This enables renewables to always be present in the energy mix.
For Residentials
Residential buildings and complexes can also benefit from the V2G technology. This technology enables buildings to rely less on the power grid and to be more self-reliant. The cost of expensive infrastructure is made lower and the majority of energy needs are satisfied through solar panels.
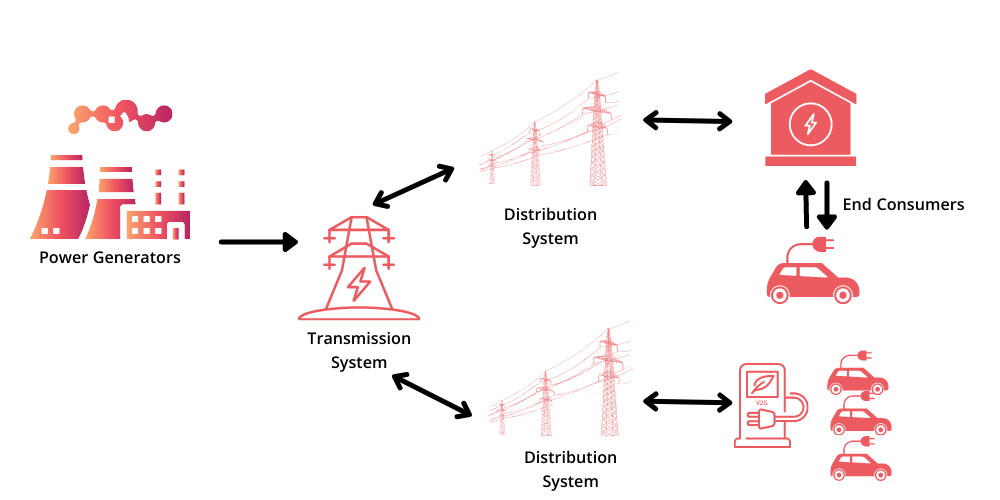
How Does Vehicle To Grid Technology Work?
The vehicle to grid technology works by using vehicle battery storage to store energy when there is an excess of it and then releases it when there is not enough energy supply. To do so, your electric vehicle needs to have access to smart charge technology and the grid needs to be equipped with a Dynamic Load Management (DLM).
Can V2G Become Mainstream?
Yes, V2G can become mainstream. The technology offers many benefits for the grid, the consumers, and residences who can also enjoy the financially beneficial feature while reducing the carbon intensity of energy production. The transportation sector can also benefit from the V2G technology.
V2G Compatible Electric Vehicles
Because bi-directional charging is a new technology, only a few EV drivers can say that their vehicles have the V2G capability:
- Nissan Leaf,
- Nissan e-NV200,
- Kia Soul, and
- Mitsubishi Outlander.
Improvement of V2G Devices
Some improvements need to be made in the battery installation on the V2G-ready vehicles. This should be done to ensure that the technology does not affect the battery life. While current research shows that the current technology does not interfere with the battery, more research is needed.
Cooperation of Energy and Car Manufacturers
To find new ways to balance energy consumption and production, new vehicle to grid-ready vehicles must be a result of cooperation between energy generators, such as power plants, and car manufacturers. Only this will ensure that the energy supply in the future is stable and that energy prices are kept at reasonable levels.
Number of Charging Stations In Your Area
Implementation of bi-directional charging on a larger scale depends on the number of EV charging stations that enable grid V2G technology in your area. The more such charging stations there are, the more stability they would introduce into the system and further decrease the reliance on fossil fuels.
FAQs
Will Tesla Offer Vehicle-To-Grid?
Yes, Tesla plans to offer Grid V2G technology in its upcoming models. A fully charged Tesla Model S Long Range Plus has 100 kWh car batteries, which are enough to travel 400 miles or power an average US household for up to 3 days. In reality, a mix of the two uses is the best solution.
Can I Plug My Electric Car Into A Regular Outlet?
Yes, you can plug your EV into a charging unit that is plugged into a regular power outlet. The downside to this kind of charging is that it takes a while.
What Are The Two Main Types Of Hybrid Vehicles?
There are two main types of Hybrid EVs:
1. The full hybrid – which has car battery storage, an electric engine, and a combustion engine. The onboard system chooses which engine to use.
2. The mid-hybrid – has both an electric engine and a combustion engine which work together to increase the mileage per gallon.
Do Electric Cars Need Oil?
No, Electric Vehicles need no oil, since there is no moving part that needs lubrication. Hybrid EVs need oil.
Conclusion
Traditional power plants are the energy source of the past. Modern EV charging in combination with solar panels and car batteries are enough to take care of your and the grid energy needs as well as reduce the carbon intensity of the energy you use. In the Grid V2G technology, your car batteries store energy from the solar panels and release it when you need it the most, introducing the grid of the 21st century.
Updated on
