How To Turn Waste Into Energy?
Did you know that food takes up the most space in the country’s landfills? That’s because the U.S. wastes more food than any other country in the world, with each household discarding around 150,000 tons of food every day. Collectively, that amounts to approximately 40 million tons of perfectly good food ending up in the trash. Additionally, we can turn this waste into energy.
Such a terrible waste, literally considering that even before the pandemic hits, around 35 million people across the country, including approximately 10 million children, experienced food insecurity. Expect those numbers to rise in 2021, with some estimates reaching as high as 50 million people resulting from the economic challenges presented by Covid-19.
Aside from being an ethical issue, food waste also takes its toll on the environment. Decaying food not only clogs up landfills but also releases methane, a potent greenhouse gas that poisons the atmosphere.
Luckily, there’s a way to turn the problem into an opportunity to solve another challenge the U.S. faces, that of providing sufficient energy for its growing population. By converting waste to energy, unwanted foodstuff that will likely make its way into rubbish dumps can serve as an energy source that will power the country’s needs.
What Is Waste Energy?

Waste energy is energy that comes from trash or garbage, otherwise known as municipal solid waste. Processing municipal solid waste (MSW) in a waste-to-energy plant transforms it into energy that can help supplement the country’s growing energy requirements.
Energy-rich materials such as plastics, paper, and products made from wood, and yard waste make up the bulk of municipal solid wastes. Every 100 pounds of MSW in the country can yield up to 85 pounds of material that can serve as fuel to generate electricity.
Combustion is the most popular way of transforming municipal waste into fuel. Burning MSW not only helps augment the country’s energy supply but is also a vital issue in waste management as it reduces the volume of materials that go into landfills.
Categorizing Food Waste
Food that would have been enough to fill the hungry bellies of around two billion people goes to waste. Wastage happens at every step of food production, from farm to table. Some of the harvests are left to rot on farms, while in markets and grocery stores blemished, but edible fruits and veggies get tossed out. In many homes, leftovers and perishables make it to the trash receptacle even if they’re still fit for consumption.
Here are some of the common foods that go to waste.
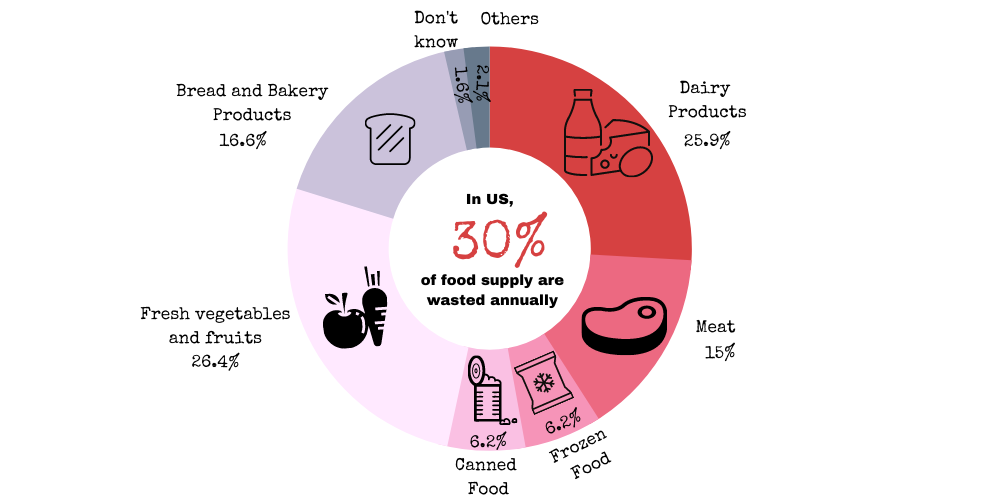
- Fruits and veggies: 51%
- Dairy products like milk, yogurt, and cheese: 50%
- Seafood, such as tuna, salmon, and shrimp: 34.7%
- Bakery products like bread and pastries: 32%
- Meat products, such as beef, chicken, and pork: 29%
Primary Sources of Food Waste
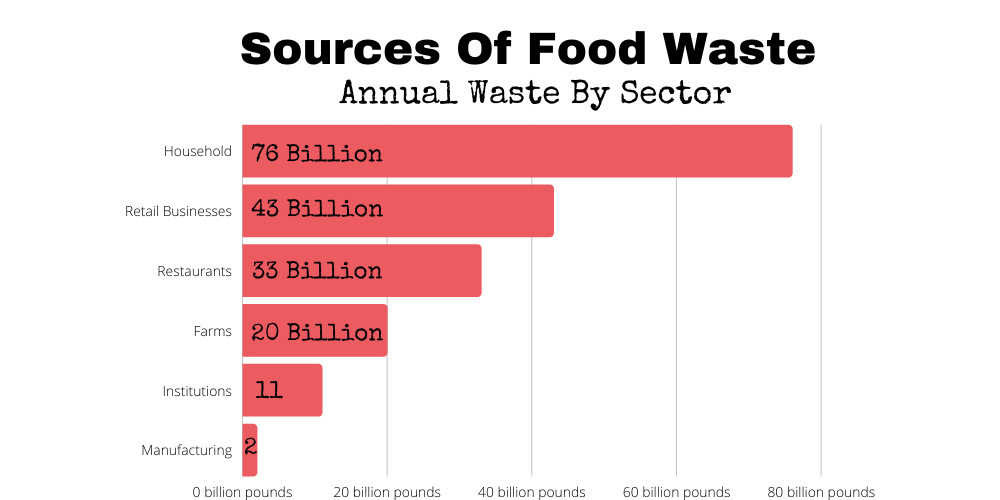
Where does the wasted food come from, you may wonder. Well, here are the top sources.
- Manufacturing facilities
- Transportation and distribution networks
- Retail business
- Restaurants and institutions
- Households
How Is Waste Converted To Energy?
Energy recovery from waste refers to the method or technique of transforming trash or garbage into electricity, heat, or fuel. The process is called waste to energy (WTE), and it involves the utilization of waste in energy plants.
There are several ways of turning trash into energy. These include:
- Combustion: This energy recovery method involves burning up waste materials at ultra-high temperatures to generate heat that then goes into electricity production.
- Gasification: Energy recovery through gasification is a process where MSW is turned into synthesized gas or syngas. In turn, syngas can be turned into transport fuels, fertilizers, or turned into electricity.
- Pyrolysis: Similar to combustion and gasification, this energy recovery method also uses elevated temperatures to turn MSW into energy. However, with pyrolysis, there’s no oxygen in the environment where the conversion takes place. As such, this method requires temperatures lower than those used in gasification and combustion. It is considered a sustainable way of producing energy from MSW.
- Anaerobic digestion: This method uses bacteria to break down organic waste, like food material, in the absence of oxygen. The process takes place in a sealed vessel that contains specialized microbe mixes that decompose (or digest) the waste.
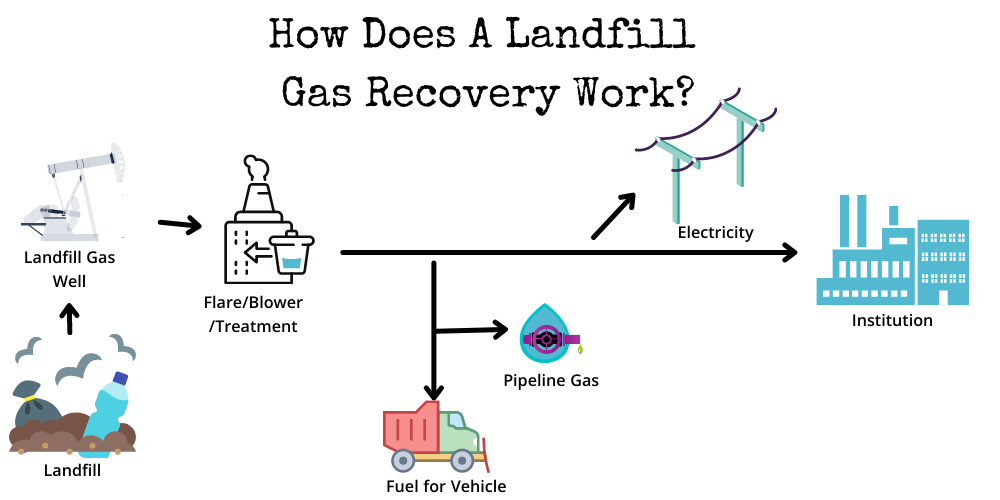
- Landfill gas recovery: This energy recovery process entails capturing the gases from municipal dumpsites and using those gases in the production of clean, renewable energy.
How The US Converts Waste into Energy
In the U.S., burning is the most common way of converting waste to energy. MSW is typically incinerated in a waste-to-energy plant that harnesses the heat produced by the combustion process and uses it to generate electricity or heat buildings. In 2019, the country’s 67 power plants burned almost 25 million tons of MSW that’s equal to 13 billion kilowatt-hours of electricity.
Methane gas that comes from decomposing garbage in large dumpsites is also used for energy production.
Countries That Convert Food Waste into Energy
Over 80% of WTE power plants are located in industrialized countries, with Germany, France, Japan, and the United States leading the pack. Fifteen percent of the trash collected is combusted for energy recovery.
How Much Energy Can Food Waste Produce?
The tons of food material that land in the country’s dumps have tremendous energy potential. If properly harnessed, instead of emitting harmful methane gas, the rubbish can turn into fuel for generating electricity.
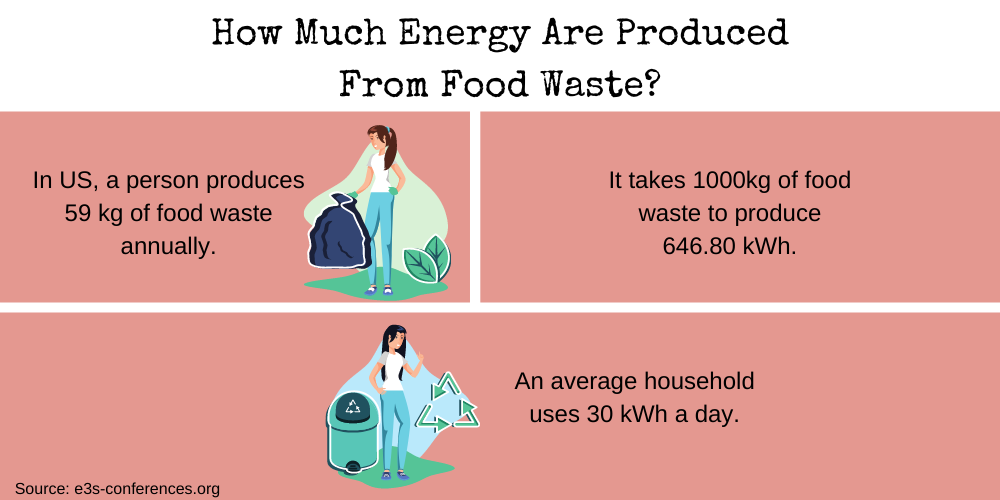
Just imagine, around a ton of food refuse can produce 300 kilowatt-hours of electricity. That’s enough energy to power thousands of homes in a year.
Waste To Energy, Is It A Good Alternative To Fossil Fuels?
Generating energy from waste is an excellent alternative to fossil fuels. In fact, WTE technology is widely recognized as one of the best ways to mitigate climate change. Just think about it. Waste that goes into dumpsites and is left to rot generates methane which pollutes the environment. But because burning the materials does not produce methane, that saves the planet from damaging greenhouse gas emissions.
Furthermore, the power generated from WTE facilities helps reduce the harmful emissions that would have come from power plants that use traditional fuel sources.
It can be said that energy from MSW is a partially renewable energy source, and as we know, renewable energy is the energy of the future.
What Are The Effects Of Waste On Energy Plants To The Environment?

The debate on whether WTE facilities bring beneficial or detrimental effects on the environment continues. Proponents of the technology assert that because WTE plants help decrease the amount of methane that goes into the atmosphere, they give Mother Nature a boost.
On the other hand, detractors insist that the pollution created by WTE plants hurt the planet just as much as or even more than emissions coming from traditional power plants. That’s because the combustion of trash spews mercury, lead, and dioxin into the atmosphere, which poses risks to both the environment and people’s health.
How You Can Contribute to Reducing Food Waste
Although there are a few other sources of food waste, almost 40% of it occurs in the home. That means if we all do our share, we can curb the amount of food that ends up in the trash and, eventually, in our dumpsites.
Here are some suggestions on how to reduce food waste.
- Make and bring along a shopping list to avoid buying foodstuff you don’t need.
- Cook only what you’ll eat. Don’t overestimate the portions.
- Make freezing a habit so you can store surplus garden harvests or bulk packages of produce.
- Compost the leftovers. Those wilted veggies can turn into nutrient-rich, low-cost fertilizers.
- Examine the contents of your refrigerator or cupboard and bring to the front foods that will expire soon.
FAQ
Why is Waste of Energy Good?
Waste to energy helps reduce the emissions of gases that harm the environment. Moreover, it augments the country’s power supply because it can generate significant amounts of energy.
What is an Example of Waste Energy?
The combustion of trash to turn it into electricity is one example of waste energy. In this process, the heat from burning materials powers turbines and generates electricity. This electricity then goes into homes, factories, and business establishments.
Why Waste to Energy is Bad?
While turning trash into energy does have some advantages, it also comes with a few drawbacks.
– It produces poisonous emissions.
– The cost is prohibitive.
– It poses risks to public health.
– Ash, a common byproduct of the technology, requires further treatment due to its toxic metals.
Final Words
Emissions that harm the environment need to be reduced. Converting garbage into energy is one of the ways to decrease the methane that comes from rotting materials. Moreover, the additional power that comes from trash also lessens the amount of electricity the country gets from fossil-fuel-based sources, which are notorious for releasing harmful gases.
Still, because of the disadvantages accompanying the waste energy technology, further research should be done to determine whether its benefits offset its adverse effects.
Developing reliable energy sources is one of the country’s goals as it seeks to fight climate change. Whether the WTE technology can move that goal forward remains to be seen as studies and debates regarding its exact value continue.
Updated on
